Applications
Home » Applications
- Applications
Induction Heating Applications
 Induction heating is a method of heating an electrically conductive material, typically metal, by using electromagnetic induction. It relies on the principle of inducing eddy currents within the material to generate heat. Those currents encounter resistance within the material, and this resistance leads to the conversion of electrical energy into heat. As a result, the material heats up rapidly and uniformly due to the internal heating effect of the eddy currents. The heating is highly localized, focusing on the part of the material within the coil or the region influenced by the magnetic field.
Induction heating is a method of heating an electrically conductive material, typically metal, by using electromagnetic induction. It relies on the principle of inducing eddy currents within the material to generate heat. Those currents encounter resistance within the material, and this resistance leads to the conversion of electrical energy into heat. As a result, the material heats up rapidly and uniformly due to the internal heating effect of the eddy currents. The heating is highly localized, focusing on the part of the material within the coil or the region influenced by the magnetic field.
Induction heating is done without physical contact on any ferrous or non-ferrous metals. The depth of penetration of the magnetic field is determined by the frequency used.
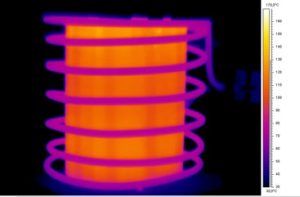
Induction heating is favored for its efficiency, speed, and precise control over temperature. It is widely used in various industrial applications, including metal hardening, annealing, forging, brazing, and even in consumer appliances like induction cooktops, where it provides rapid and energy-efficient cooking by directly heating the cookware.
There are many of these applications that induction heating can benefit in your facility. Here are just a few:
- Heat Treating (Hardening/Annealing/Tempering)
- Hot Heading/Wire Heating
- Crystal Growing
- Brazing/Soldering
- Forging/Hot Forming
- Shrink Fitting
- Melting
- Preheat to Welding
- Bonding/Curing
- Patch Coating


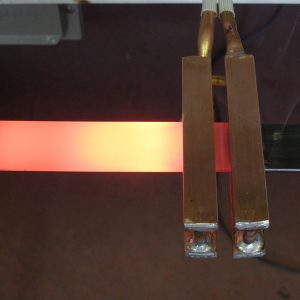


 Due to the precise and repeatable process induction heating provides,
heat treating is a great use for this equipment. Whether you need a specific Rockwell hardness or if you just need to soften the metals, induction heating is the way to go.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT HEAT TREATING
Due to the precise and repeatable process induction heating provides,
heat treating is a great use for this equipment. Whether you need a specific Rockwell hardness or if you just need to soften the metals, induction heating is the way to go.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT HEAT TREATING 



 Induction heating is widely used in the hot heading/wire heating field. Its specific in the aerospace fastener industry as well as in the automotive industry. The use of induction prolongs the life of the dies in machines, saving the customer money.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT HOT HEADING
Induction heating is widely used in the hot heading/wire heating field. Its specific in the aerospace fastener industry as well as in the automotive industry. The use of induction prolongs the life of the dies in machines, saving the customer money.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT HOT HEADING 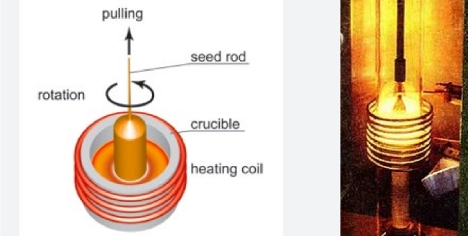 Induction is being used more and more for the crystal growing process, due to the cost savings and efficiency it offers. With the control Induction offers with the precise temperatures, the cleanliness and non-contact ways of heating, allows for less waste then the older traditional ways of crystal growing methods.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT CRYSTAL GROWTH
Induction is being used more and more for the crystal growing process, due to the cost savings and efficiency it offers. With the control Induction offers with the precise temperatures, the cleanliness and non-contact ways of heating, allows for less waste then the older traditional ways of crystal growing methods.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT CRYSTAL GROWTH 



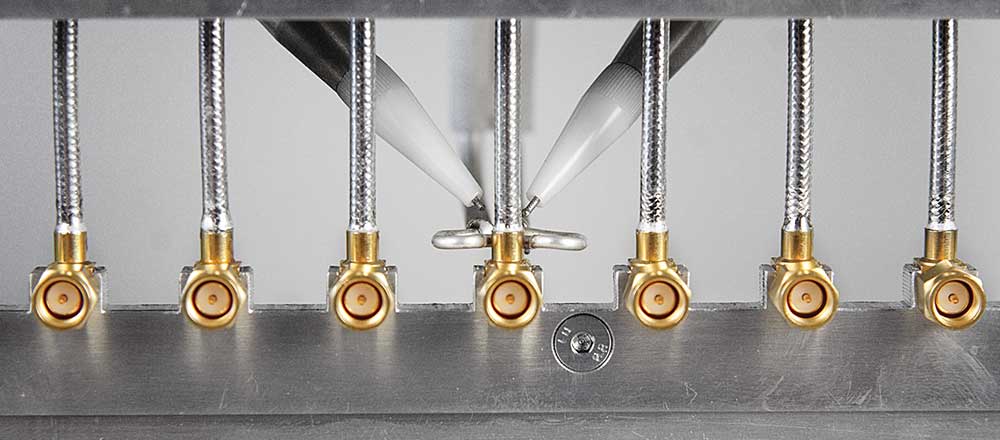 Whether its brazing or soldering, Induction heating is yet another great tool for this application. With the localized heating and repeatability these machines offer and takes away the guest work from the operator.
(We also offer brazing automation which you can find on our Services page.)
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT BRAZING/SOLDERING
Whether its brazing or soldering, Induction heating is yet another great tool for this application. With the localized heating and repeatability these machines offer and takes away the guest work from the operator.
(We also offer brazing automation which you can find on our Services page.)
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT BRAZING/SOLDERING 




 Induction is a quick and efficient way to heat a part that is being forged or hot formed. A furnace could take hours, while induction could take seconds to minutes. We also offer Pyrometers/IR Sensors to maintain a temperature allowing for a uniform heat throughout the part.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT FORGING/HOT FORMING
Induction is a quick and efficient way to heat a part that is being forged or hot formed. A furnace could take hours, while induction could take seconds to minutes. We also offer Pyrometers/IR Sensors to maintain a temperature allowing for a uniform heat throughout the part.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT FORGING/HOT FORMING 
 This is a quick and precise way to heat a specific part to use in a shrink fitting application. With the use of a Pyrometer/IR Sensor, we can hold a temperature allowing the housing to expand, while the other part can be inserted with no problem. After cooling both parts are secure with no further actions required.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT SHRINK FITTING
This is a quick and precise way to heat a specific part to use in a shrink fitting application. With the use of a Pyrometer/IR Sensor, we can hold a temperature allowing the housing to expand, while the other part can be inserted with no problem. After cooling both parts are secure with no further actions required.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT SHRINK FITTING 
 Melting is a great application for Induction Heating. It offers the low-cost expenses compared to ovens or furnaces which must run all day long to keep the specific temperature.
With induction, the process is quick and precise to the melting temperature you require. The ease of heating up graphite crucibles to melt any metal you prefer.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT MELTING
Melting is a great application for Induction Heating. It offers the low-cost expenses compared to ovens or furnaces which must run all day long to keep the specific temperature.
With induction, the process is quick and precise to the melting temperature you require. The ease of heating up graphite crucibles to melt any metal you prefer.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT MELTING 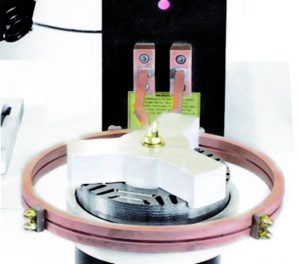
 Curing is an important step in the manufacturing process for many materials, as it helps to ensure that the finished product has the desired properties and will be able to withstand the stresses and strains it will be subjected to in its intended use.
The temperature and duration of the curing process will depend on the specific material being cured and the desired properties of the finished product.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT CURING
Curing is an important step in the manufacturing process for many materials, as it helps to ensure that the finished product has the desired properties and will be able to withstand the stresses and strains it will be subjected to in its intended use.
The temperature and duration of the curing process will depend on the specific material being cured and the desired properties of the finished product.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT CURING 

 In patch coating for manufacturing, once the patch powder is blown onto the threads. Maintaining precise temperature control is crucial to ensure the powder melts and adheres correctly to the threads. Striking the right temperature balance is essential; excessive heat can burn the powder, while insufficient heat prevents proper adhesion.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT PATCH COATING
In patch coating for manufacturing, once the patch powder is blown onto the threads. Maintaining precise temperature control is crucial to ensure the powder melts and adheres correctly to the threads. Striking the right temperature balance is essential; excessive heat can burn the powder, while insufficient heat prevents proper adhesion.
REQUEST A QUOTATION
LEARN MORE ABOUT PATCH COATING