Induction Heating Best Practices: Tips for Successful Hot Heading Operations
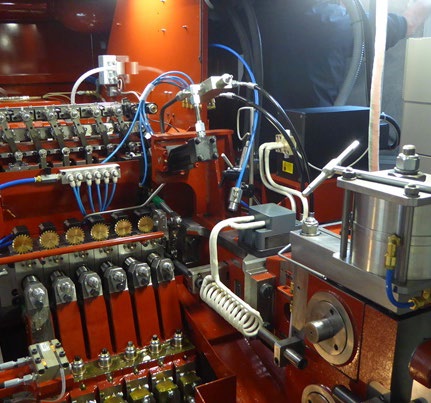 Hot heading can refer to a few different processes depending on the context, but it generally involves the shaping or forming of metal or other materials at an elevated temperature.
Hot heading can refer to a few different processes depending on the context, but it generally involves the shaping or forming of metal or other materials at an elevated temperature.
In metalworking, hot heading allows for metal to be pressed or forged into a specific shape using a die or a punch. This process is commonly used in the manufacture of fasteners, such as bolts and screws, where the heated metal is formed into the desired head shape.
Imagine a bolt head or other fastener: The actual piece needs to be molded in a certain way to fit certain parameters for your customers. Induction heating can rapidly raise temperatures and allow for that work to happen with precision (and with minimal material waste).
Whatever your end product may be, induction heating technology can supply an easily controllable vehicle for your hot heading needs.
Let’s talk best practices.
Equipment Selection
First, and critically, you must choose the right induction heating equipment, including the appropriate induction coil, power supply, and frequency, based on the size and material of the workpiece. Ensure that the equipment is capable of delivering the required power for efficient heating.
What’s your end goal? Work backward from your desired end product and decide what equipment you’ll need to get the job done at scale. Build in allowances for expansion down the line, too.
Temperature Control and Monitoring
It’s important that you implement precise temperature control and real-time monitoring of the induction heating process. Use temperature sensors and feedback systems to maintain the workpiece at the desired temperature, ensuring consistency and quality.
While automation can certainly play a role, your team must be in touch with the actual hot heading process.
It’s helpful to continuously analyze data and to monitor processes, such as temperature control and monitoring, to identify areas for improvement. Seek opportunities to optimize the hot heading process, such as by adjusting power settings, heating durations, or coil configurations to increase efficiency. There’s always room for improvement!
Material Selection
Select the right materials for hot heading that are compatible with induction heating. Consider factors such as material composition, size, and magnetic properties, which can affect heating efficiency.
Proper Workpiece Handling
Position the workpiece accurately within the induction coil to ensure uniform heating. Adequate spacing and alignment are crucial to prevent overheating or uneven heating.
This is another reason why it’s critical to choose the right equipment from the jump (see our earlier point).
Energy Efficiency
Minimize energy consumption by using high-frequency induction heating when appropriate and by ensuring that equipment is well-maintained.
You’ll want to select the appropriate frequency based on the size and material of the workpiece; higher frequencies are often more suitable for smaller components. (Low frequencies in induction heating are generally suitable for larger workpieces or applications where deeper heat penetration is required.)
WANT TO LEARN MORE ABOUT HOT HEADING? GET IN TOUCH TODAY
 Quality Assurance and Testing
Quality Assurance and Testing
Implement rigorous quality control measures, including inspections and testing, to ensure the integrity of hot-headed components. Regularly test samples to verify that they meet the required specifications.
Don’t forget to revisit your SOPs! Everyone on your team must understand the QA measures that guide your process, and those measures must be kept up-to-date as technology advances and as new safety regulations are published.
Safety Considerations
This might go without saying, but we’ll say it: Prioritize safety when operating induction heating equipment.
Ensure that personnel are trained in safe handling procedures and that appropriate safety measures, such as protective gear and emergency shutdown systems, are in place.
When you revisit your SOPs, that might be a good time to also revisit basic safety protocols in your facility.
Maintenance and Servicing
Establish a regular maintenance schedule for induction heating equipment.
Maintain the coils, power supplies, and cooling systems to extend the lifespan of the equipment and prevent unplanned downtime.
At the time of installation, make sure you communicate clearly with your equipment provider.
Training and Skill Development
Invest in employee training to ensure that operators have the necessary skills and knowledge to operate induction heating equipment effectively. Training should cover equipment operation, safety protocols, and troubleshooting.
Proper Cooling
Implement efficient cooling systems to manage the heat generated during the hot heading process. Cooling should be sufficient to prevent overheating of the equipment and ensure consistent performance.
Documentation
Maintain thorough records of the induction heating process parameters, quality control results, and equipment maintenance. These records are valuable for process validation and troubleshooting.
By following these best practices, businesses can optimize their hot heading operations using induction heating, resulting in improved efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
It’s important to adapt these practices to specific industry requirements and the characteristics of the materials being processed.